Background
Depending on the degree you are studying you may already be familiar with either design or hardware or software development and you may also have already completed a team project course but now you are flying solo.
There is a lot to think about when developing a new product from scratch. How do you manage your project, what needs to be done by when and in what order? Remember the ten project management knowledge areas (scope, time, cost, quality, human resources, procurement, risks, communication, integration and stakeholder management) from your past lectures? Well, this is where it all comes together and you alone are responsible for the outcome. Maybe a little frightening at first but the following list might help you to get started and to produce a professional product in the end.
There may be other things you will need as well, please let me know if you have found some other resource that you would like me to share here.
This is a technical site, the ITEE Thesis Site has been prepared by UQ to answer any administrative questions for you.
From design to deployment
Development MethodologyManagement
You may be familiar with the Waterfall Software Development Methodology and may also have heard about different Agile frameworks such as Scrum that have found recent adaptation not only in the software industry.
When you enter the workplace today you will probably be assigned to a Scrum team so why not getting familiar with it by using Scrum in this project.
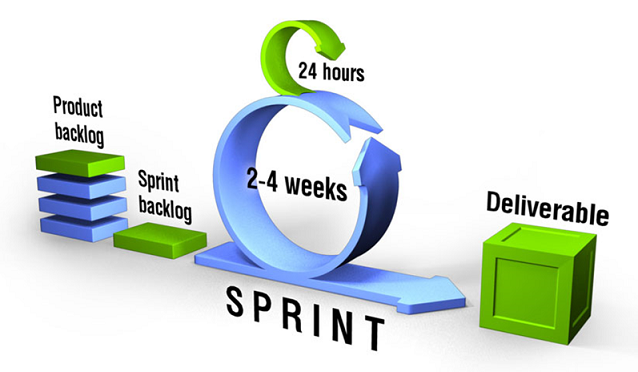
Scrum is a simple, people-centric framework for managing work that is based on the values of honesty, openness, courage, respect, focus, trust, empowerment, and collaboration. We will be using the Scrum framework to develop our project not only for the purpose of learning about it but also to make our life easier by doing twice the work in half the time (you should listen to the audio book).
You can get the Official Scrum Guide from the Scrum Guide Website created by Jeff Sutherland and Ken Schwaber, the creators of Scrum. If you want to find out how it is implemented you can watch several videos on Scrum Training and have a look at this Scrum Reference Card.
Effort is measured in story points and here is an example of a Burndown Chart, the page contains a link to an Excel spreadsheet that you can use to create the chart. You will get better at estimating every time you complete a sprint.
To keep track of your user stories, tasks, work in progress, tasks done and potentially shippable products we use Trello as a Scrum Board, it was made for this purpose.
Once you enrol into your course I will invite you to the myThesis Trello board via your student email address. Please have a look at the "Example Scrum Board" of the "myThesis Organisation" I prepared in Trello. Please setup a Scrum board for your project using your Project's name in the "myThesis Organisation".Access to the Electronics Engineering LaboratoryManagement
You can use the ITEE GP Thesis Laboratory (47-401), the ITEE Thesis Lab (78-108) and the ITEE Physical Design Workshop (78-207) for developing your project. The ITEE GP Thesis Laboratory has solder stations, power supplies, oscilloscopes and a desk to work on. To be able to use these rooms you have to request access. Here are the interactive floorplans (UQ login required) with more detail.Selecting HardwareDesign
There are several Australian and overseas hardware suppliers that you can order from. Here is a list of the most popular suppliers Little Birds Electronics (Australia), Sparkfun (US with distributors in Australia), Adafruit (USA) and Seeedstudio (China). They all have great websites and Adafruit has many YouTube videos and example project ideas including code.Ordering HardwareDesign
Your hardware order has to be submitted via the UQ ITEE ETSG using their new ordering system. Careful when ordering from overseas, you have to convert to local currency and add delivery costs!Circuit diagramDesign
 You can use
Fritzing
to create a circuit diagram from your breadboard design and
turn it into a professional PCB directly from your Fritzing sketch.
Fritzing comes with a library of electronic part bins already installed.
A bin contains parts made by a specific manufacturer such as Sparkfun.
These hardware suppliers have an
Adafruit Fritzing Github repo and
Sparkfun Fritzing Github repo
for housing their parts or new parts that are not yet in Fritzing.
You can use
Fritzing
to create a circuit diagram from your breadboard design and
turn it into a professional PCB directly from your Fritzing sketch.
Fritzing comes with a library of electronic part bins already installed.
A bin contains parts made by a specific manufacturer such as Sparkfun.
These hardware suppliers have an
Adafruit Fritzing Github repo and
Sparkfun Fritzing Github repo
for housing their parts or new parts that are not yet in Fritzing.
If you want to use the Altium Designer software (available on the PCs in the UQ labs) you can watch the following videos to learn how to use it:
- Altium Tutorial Part 1 - Schematics
- Altium Tutorial Part 2 - PCB
- Altium Tutorial Part 3 - Custom Components
3D PrintingDesign
 You may wish to 3D print a special part or housing for your project.
The UQ Social Sciences & Humanities (SS&H) library has a 3D printer that all UQ students can use. You design your model in
SketchUp,
pay $5 via your credit card through their
website,
specify a single print colour for your model,
submit your STL file and you will get an email when it's ready to be picked up.
Your printing time is limited to four hours per job.
You can watch the printing process by visiting the SS&H library (Bar Merlo entrance opposite the IT Help desk),
a webcam may be installed in the near future.
You may wish to 3D print a special part or housing for your project.
The UQ Social Sciences & Humanities (SS&H) library has a 3D printer that all UQ students can use. You design your model in
SketchUp,
pay $5 via your credit card through their
website,
specify a single print colour for your model,
submit your STL file and you will get an email when it's ready to be picked up.
Your printing time is limited to four hours per job.
You can watch the printing process by visiting the SS&H library (Bar Merlo entrance opposite the IT Help desk),
a webcam may be installed in the near future.
If you are using the SketchUp "Solid Tools" keep in mind that they will expire after one month of using the free version and are only available in SketchUp Pro.
 You can find out a bit more about how your model is printed and how long it will take to print by downloading the
MakerBot software (used to print 3D models with).
You can open your STL file in it without having a 3D printer attached and it will show you what the
automatically created support structures for any "overhanging parts" will look like that will prevent the
sagging of the plastic when it is still warm and that you have to
break off after receiving your hardened printed model.
You can find out a bit more about how your model is printed and how long it will take to print by downloading the
MakerBot software (used to print 3D models with).
You can open your STL file in it without having a 3D printer attached and it will show you what the
automatically created support structures for any "overhanging parts" will look like that will prevent the
sagging of the plastic when it is still warm and that you have to
break off after receiving your hardened printed model.
Simple plastic box casingBuild
If you want to make a simple plastic box (mandatory if you are working with a power supply with exposed 240V terminals), you can design your box using MakerCase and supply the resulting Laser Cutter Plan file to the UQ ITEE ETSG who will cut one-off's for you. Don't forget to add holes for cable grommets and screw holes for feet etc.
Online helpBuild
Two great sources of information that always pop up in search results are worthwhile mentioning here: Stackoverflow allows you to post questions and W3Schools lets you explore example code via a Try it Yourself editor.Arduino programming environmentBuild
 You can use the latest version of the official
Arduino IDE.
There are some installation instructions on the
Sparkfun and
Adafruit websites.
A different IDE containing a debugger can be found on the
CodeBlocks website.
You can use the latest version of the official
Arduino IDE.
There are some installation instructions on the
Sparkfun and
Adafruit websites.
A different IDE containing a debugger can be found on the
CodeBlocks website.
Webapp programming environmentBuild
You may prefer to use an IDE you are already familiar with, I find Netbeans contains all the features I need and it might be a little easier to learn than Eclipse.Webapp programming languagesBuild
If you are working on an IoT project you are connecting your Arduino to the Cloud to access a database. Your users will then need a webapp to communicate with this database so that they can see the data from your device and also maybe communicate with it to say configure it. The myThesis webapp, which you are using now, serves two purposes, it provides you with some resources required for your thesis project but also demonstrates how a webapp could look like for your project.
 Your webapp will be written in
PHP.
You have to
install PHP
on your local development machine so that your local webserver can run it, it is already
installed on your UQ ITEE SmartOS zone.
Your webapp will be written in
PHP.
You have to
install PHP
on your local development machine so that your local webserver can run it, it is already
installed on your UQ ITEE SmartOS zone.
 You will also use
jQuery mobile
to create a professional looking user interface for your webapp.
You can use the jQuery
Themeroller
to style it.
You will also use
jQuery mobile
to create a professional looking user interface for your webapp.
You can use the jQuery
Themeroller
to style it.
GIT code repositoryBuild
 When developing your code and documentation you have to store your files in a code repository.
This will not only enable you to backup everything to guard your work from accidental loss
but also allow you to implement version control and to create
code branches.
GIT is a distributed code repository and version control system that allows groups of developers to work together on the same code base.
When developing your code and documentation you have to store your files in a code repository.
This will not only enable you to backup everything to guard your work from accidental loss
but also allow you to implement version control and to create
code branches.
GIT is a distributed code repository and version control system that allows groups of developers to work together on the same code base.
As part of the enrollment in this course the School will provide you with a private GIT repository with the name myThesis-sXXXXXXX (where sXXXXXXX is your UQ username). You will have to create a local repository on your development machine and you will push and pull files to and from this local repository to the central School repository. It is important for you to store your work in a private repository so that you cannot be accused of collusion/plagiarism.
It is best to use a graphical interface instead of the GIT command line. For both Windows and Mac OS X SourceTree is recommended but instructions for GITextensions are also included below.SourceTree
You will need to download and install Sourcetree first. You will also be required to create an account with Atlassian. Here are some instructions on how to use SourceTree to Commit, Push, and Pull a repository.Windows Users
- Launch SourceTree and select File > Clone / New
- As your Source Path / URL enter the ITEE Repository URL found here (UQ login required) You want the Git clone/push HTTP URL (case sensitive).
- Enter your UQ username and password into the SourceTree popup window when prompted.
- Choose the destination path for where you would like your local copy of the repository to be stored
- Click Clone
Mac OS X Users
- Launch SourceTree, click + New Repository and choose Clone from URL
- As your Source URL enter the ITEE Repository URL found here (UQ login required) You want the Git clone/push HTTP URL (case sensitive).
- Enter your UQ username and password into the SourceTree popup window when prompted.
- Choose the destination path for where you would like your local copy of the repository to be stored
- Click Clone
GITextensions
You will need to download and install GIT (command line only, here is a nice interactive tutorial) and the GITextensions (Windows interface to GIT), you will also need kdiff3 which is used by GIT to compare text files. Once you have installed all this follow these steps (use PuTTY, not OpenSSH when given the choice).
- First create a new (personal) repository on your machine via the Start->Create new repository... menu item in GITextensions.
- You will require SSH authentication for GITextensions to connect to your remote repository, so now Generate a public/private key pair (SSH-2 RSA) in GITextensions via the menu items Tools->PuTTY->Generate or import key and save them to your machine (note that Pageant, the PuTTY authorisation agent, is now running in the background).
- Then copy the private key and paste it into here (UQ login required) for use with your School repository.
- Now you have to tell GITextensions how to connect to your School repository. This page (UQ login required) tells you the SSH protocol location, enter it into the Url field of Repository->Remote repositories..., browse to your Private key file, load the SSH key and save the changes. When you test the connection the only reply should be Using username "sXXXXXXX. no command?"
To access your repo from your Netbeans IDE use this guide or follow this discussion if you are using Eclipse.
Local webserverBuild
When developing your server side code you need to test your PHP scripts on your development machine first using a local webserver before you deploy anything to your Internet webserver such as your UQ ITEE SmartOS zone. QuickPHP is a lightweight webserver (for Windows) with a minimum of configuration options that works great.Database administrationBuild
You can design and maintain your mySQL database (on your local development machine) using mySQL Workbench, for your server database you will use phpMyAdmin which is already installed on your UQ ITEE SmartOS zone.Accessing your DatabaseBuild
Once your database is setup you access it with your PHP code running on the server (the same code that dynamically constructs your HTML page, including any JavaScript, before all this is sent to the client browser). There are three different APIs for accessing a mySQL database:- mysql (DO NOT USE - is deprecated!)
- mysqli (MySQL Improved - procedural and object-oriented versions available)
- PDO (PHP Data Objects - object-oriented only, virtually eliminates the risk of SQL injections) and can also be used for other than mySQL databases
Debugging client codeBuild
Since your code is spread over the server (PHP) and the client (JavaScript) you need to be able to debug both ends. Your chosen IDE (Netbeans or Eclipse) will already have the ability to set breakpoints in your server code to inspect variables. You can do the same for your client code by using tools build into your browser such as the Firebug plugin or Chrome DevTools.Creating password access to your webappBuild
You will probably want the users of your product to log into your webapp so that everybody can maintain their own private data. The simplest way to do this would be to use the person's email address as the username since it is guaranteed to be unique and the user will most likely remember it. Asking the user for just an email address in the registration process avoids annoying completion of lengthy forms and gives you an easy way to communicate with your user in case they forget their password. You could get other information such as their country/region or language from their IP address and their browser respectively if you need to switch to a different language or currency in your webapp automatically. As a verification step you can now send your new user an email with an automatically generated password. If you want to get sophisticated you could put a time window on how long this password is valid and/or ask the user to change it immediately when logging in next time.
Don't forget the Forgot password link. It should issue a new password to the email address of the user following the same process you implemented for the registration procedure.
Never ever store a password in clear text in your database. Users often re-use passwords for other applications and I read nearly every day about yet another database that has been hacked. The password should be salted and hashed so not even the database administrator can see what it is or reverse-engineer it. Here is a great explanation of how this can be achieved including some scripts in PHP and other languages here that you can first study and understand and then re-use in your own webapp and cite in your documentation.
Sending emails from PHPBuild
If you want to send emails to your user from PHP (e.g. for your forgot password link) you can use PHPMailer, here is a tutorial.Creating graphsBuild
You can create graphs on the server with PHP and then include the resulting image into your webpage (JpGraph does this). A better solution would be to let the client do the work to save you processing time and bandwidth usage. This allows your graphs to be dynamic and interactive as well. There are lots of JavaScript graphics libraries around that let you do this.
 This site has a nice comparison tool that
lets you select the type of graph you need, the pricing scheme and other options.
Cost is important to consider since the library might be free for non-profit use but
may have a hefty price tag for commercial use so ensure that it is also legal to use
a free product commercially. Considering all this and the fact that you are already using jQuery mobile
which is based on jQuery
jqPlot might be a good solution if it can produce the
graph type you need.
This site has a nice comparison tool that
lets you select the type of graph you need, the pricing scheme and other options.
Cost is important to consider since the library might be free for non-profit use but
may have a hefty price tag for commercial use so ensure that it is also legal to use
a free product commercially. Considering all this and the fact that you are already using jQuery mobile
which is based on jQuery
jqPlot might be a good solution if it can produce the
graph type you need.
WiFi for your deviceBuild
 If you want to connect your mobile IoT or Wearable to the Internet using WiFi I suggest you have a look
at the
ESP8266, it only cost US$9.95
(US$6.95 without the break-out board)
and consists of an 80 MHz microcontroller with a full WiFi front-end (both as client and access point,
this means you can serve webpages from it to your user's smart phone or computer)
and TCP/IP stack with DNS support, i.e. you
don't need an Arduino at all anymore for your project. It only has one analog input pin but there is a
way around this limitation.
These
PDF instructions
will get you started.
If you want to connect your mobile IoT or Wearable to the Internet using WiFi I suggest you have a look
at the
ESP8266, it only cost US$9.95
(US$6.95 without the break-out board)
and consists of an 80 MHz microcontroller with a full WiFi front-end (both as client and access point,
this means you can serve webpages from it to your user's smart phone or computer)
and TCP/IP stack with DNS support, i.e. you
don't need an Arduino at all anymore for your project. It only has one analog input pin but there is a
way around this limitation.
These
PDF instructions
will get you started.
The ESP8266 has recently (2016) been replaced with a more advanced version, the ESP32. It has dual processors, is faster, has an integrated dual mode Bluetooth (classic and BLE) module, 32x GPIOs including 12 ADC input channels and heaps more. Kolban's Book on the ESP32 is a treasure trove of information on the ESP32 and many peripherals.
You cannot connect the ESP's to a LAN that uses enterprise encryption (a network that requests username/password like UQs), however the ESP32 might offer this in a future version, but you can create a WiFi access point (AP) on your Internet connected Windows machine or your smart phone and then connect the ESP8266 to this AP. You can also convert a wireless router into an AP.LoRaWAN for your deviceBuild
 A Long Range Wide Area Network (LoRaWAN) is a Low-Power Wide-Area Network (LPWAN) developed by the
LoRa Alliance specifically for the
Internet of Things (IoT). LoRaWAN will provide your device with low-speed/low-bandwidth network access from up
to 16km (line of sight) away using minimal power consumption (deep in-building penetration is 2 km).
We have installed a LoRaWAN Gateway at UQ St Lucia campus for your project and you will receive a
MTUDK2-ST-MDOT Developer Kit if you need
to integrate LoRaWAN into your project to connect your IoT device to your UQ server and database. Using this
development kit you can program an Arduino to use the mDot module as a wireless interface or program
the ARM processor on the
mDot
directly to use its 12 bit ADC with 11 channels and up to 21 GPIOs. A mDot Pinout Diagram can be found
here.
You can use
Eclipse
or the
ARMmbed cloud service (create account first)
to program the mDot.
A Long Range Wide Area Network (LoRaWAN) is a Low-Power Wide-Area Network (LPWAN) developed by the
LoRa Alliance specifically for the
Internet of Things (IoT). LoRaWAN will provide your device with low-speed/low-bandwidth network access from up
to 16km (line of sight) away using minimal power consumption (deep in-building penetration is 2 km).
We have installed a LoRaWAN Gateway at UQ St Lucia campus for your project and you will receive a
MTUDK2-ST-MDOT Developer Kit if you need
to integrate LoRaWAN into your project to connect your IoT device to your UQ server and database. Using this
development kit you can program an Arduino to use the mDot module as a wireless interface or program
the ARM processor on the
mDot
directly to use its 12 bit ADC with 11 channels and up to 21 GPIOs. A mDot Pinout Diagram can be found
here.
You can use
Eclipse
or the
ARMmbed cloud service (create account first)
to program the mDot.
MQTT and Mosquitto broker for LoRaWANBuild
 MQTT
(Message Queuing Telemetry Transport) is a lightweight client/server publish/subscribe messaging transport
protocol. It requires a broker which is responsible for distributing messages to interested clients based on
the topic of a message.
Mosquitto is an open source MQTT broker implementation that you can install on your PC or MAC from
here
to get familiar with it. An extensive description of MQTT can be found
here
and a short description of MQTT features can be found
here.
You can download and install an application called
MQTTBox
to publish topics and subscribe to them to test out your private mosquitto broker installation or use the
broker supplied by Eclipse at iot.eclipse.org:1883 (1883 is the MQTT port).
Here are three screenshots showing the MQTTBox parameters for
client setup,
publisher and subscriber
configuration
and resulting
output
after a message has been published, this may help you with your first test.
MQTT
(Message Queuing Telemetry Transport) is a lightweight client/server publish/subscribe messaging transport
protocol. It requires a broker which is responsible for distributing messages to interested clients based on
the topic of a message.
Mosquitto is an open source MQTT broker implementation that you can install on your PC or MAC from
here
to get familiar with it. An extensive description of MQTT can be found
here
and a short description of MQTT features can be found
here.
You can download and install an application called
MQTTBox
to publish topics and subscribe to them to test out your private mosquitto broker installation or use the
broker supplied by Eclipse at iot.eclipse.org:1883 (1883 is the MQTT port).
Here are three screenshots showing the MQTTBox parameters for
client setup,
publisher and subscriber
configuration
and resulting
output
after a message has been published, this may help you with your first test.
The LoRaWAN gateway at UQ comes with an inbuilt mosquitto broker that we will use to publish IoT messages with,
it needs a username/password.
3G SIM card for your deviceBuild
 If you want to connect your mobile IoT or Wearable to the Internet without using WiFi you need the
relevant circuitry first.
We will use the
XC4221 GPRS/GSM shield for Arduino from from Jaycar/Electus.
It is approved for use in Australia and contains the
SIM900 GSM module which is 2G.
2G is being phased out in Australia and Telstra will not be providing a 2G service anymore after December 2016.
Do not purchase any 3G US breakout boards or other imported 3G boards since most of the imported hobby boards are not certified for use in Australia.
We are presently trying to find a certified 3G shield/module that we can use with Telstra after December 2016.
If you want to connect your mobile IoT or Wearable to the Internet without using WiFi you need the
relevant circuitry first.
We will use the
XC4221 GPRS/GSM shield for Arduino from from Jaycar/Electus.
It is approved for use in Australia and contains the
SIM900 GSM module which is 2G.
2G is being phased out in Australia and Telstra will not be providing a 2G service anymore after December 2016.
Do not purchase any 3G US breakout boards or other imported 3G boards since most of the imported hobby boards are not certified for use in Australia.
We are presently trying to find a certified 3G shield/module that we can use with Telstra after December 2016.
Second you will need a SIM card for your data transfer (i.e. without voice calls). We will be using SIM cards from an Australian organisation specialised in machine to machine (M2M) communication M2Mone (allows SMS to be sent and received as well as data). M2M uses Telstra as a data carrier and has a very nice web control centre M2M One Control Centre User Guide (pdf).
There are presently three different sizes for SIM cards: Full size SIM, Micro SIM and Nano SIM. M2Mone also offers (surface mounted/solderable SIM chips).
Here is a nice article about Australian Mobile Network Frequencies in case you are interested in this.
UQ webserver (SmartOS zone)Deploy
To deploy your webapp you will need access to a web/database server. As part of the enrollment in this course the School will provide you with a UQ ITEE web project smartOS (a UNIX-like OS) zone that you have root access to for the duration of your project. A Web Project zone comes pre-installed with PHP and mySQL. This guide (UQ login required) explains what is installed on your zone by default and how to manage your zone.
If you need command line access to your zone you need PuTTY (the name "PuTTY" has no definitive meaning) but normally you would only need file access to upload your website files to your zone. Download, install and run SSHFS (Secure SHell FileSystem) to mount a network drive as /var/www/htdocs and create your webapp files and directories there. You will then be able to browse to them via http://sXXXXXXX.uqcloud.net. You can also use FileZilla to upload your files if you are already familiar with it (use the SFTP protocol and the Normal logon type). If, during the installation of SSHFS onto a Windows OS newer than XP, you get an error message related to a Dokan version mismatch, right-click the installer file, select properties then compatibility and check run this program in compatibility mode for Windows XP SP3, it will work now.
Zones and their filesystems can only be accessed from within UQ or via VPN (UQ login required) but you can request your zone to be opened up to the Internet (i.e. for demonstrations to your client). To run phpMyAdmin on your zone, in order to maintain your production database, browse to http://sXXXXXXX.uqcloud.net/phpmyadmin/index.php.
Tuning your webappDeploy
To provide your users of your webapp with the best possible experience you should consider increasing the browser load speed via minification and compression which will also reduce data cost on mobile devices and increase your ranking in Google. If Google sees that your webpage does not load well for certain devices such as phones, ipads, etc. they won't include you in the results because Google doesn't want to send users to slow pages.
Minification refers to the process of removing unnecessary or redundant data from your JavaScript code and stylesheets without affecting how the resource is processed by the browser - e.g. code comments and formatting, removing unused code, using shorter variable and function names, and so on (Google developers). Here are a few online services for CSS and JavaScript & CSS.
Other ways to speed up loading your webapp is via gzip compression (which must be configured on your server via the .htaccess file), deferring render blocking javascript and many more.